 REHYB@SSSA: The powered shoulder-elbow exoskeleton NESM-gamma - 24.06.2022. Designing a robotic exoskeleton for rehabilitating or assisting human motor functions is a big engineering challenge. Exoskeletons can support complex human movements by providing timely and precise assistive actions according to the user’s intention while preserving the natural movement biomechanics.
REHYB@SSSA: The powered shoulder-elbow exoskeleton NESM-gamma - 24.06.2022. Designing a robotic exoskeleton for rehabilitating or assisting human motor functions is a big engineering challenge. Exoskeletons can support complex human movements by providing timely and precise assistive actions according to the user’s intention while preserving the natural movement biomechanics.  REHYB@SK: Stakeholder workshop on User Interface and serious gaming applications - 22.04.2022. A successful design of our ReHyb device has to meet the wishes and needs of the patients and adjunct stakeholders. That’s why we emphasize a user-centered approach within the ReHyb project. Being one of the clinical partners in the ReHyb project, Schoen Clinic Bad Aibling-Harthausen (SK) aims to provide the perspective from users and clinical stakeholders such as medical professionals (e.g. medical doctors, therapists), patients in the clinic and at home and their caregivers.
REHYB@SK: Stakeholder workshop on User Interface and serious gaming applications - 22.04.2022. A successful design of our ReHyb device has to meet the wishes and needs of the patients and adjunct stakeholders. That’s why we emphasize a user-centered approach within the ReHyb project. Being one of the clinical partners in the ReHyb project, Schoen Clinic Bad Aibling-Harthausen (SK) aims to provide the perspective from users and clinical stakeholders such as medical professionals (e.g. medical doctors, therapists), patients in the clinic and at home and their caregivers.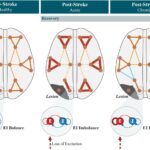 REHYB@IBEC: Large-scale modeling of the human cortex may help understand the processes of recovery in stroke patients - 30.03.2022. The mechanisms by which focal brain lesions such as stroke affect brain areas away from the lesion, causing a wide loss of functional activity ranging from motor to cognitive function, are not completely understood and are still unresolved.
REHYB@IBEC: Large-scale modeling of the human cortex may help understand the processes of recovery in stroke patients - 30.03.2022. The mechanisms by which focal brain lesions such as stroke affect brain areas away from the lesion, causing a wide loss of functional activity ranging from motor to cognitive function, are not completely understood and are still unresolved. REHYB@DTU: Exploration of VR and AR capabilities for serious game rehabilitation - 22.02.2022. Developing new interfaces for rehabilitation requires the exploration of different technology platforms and their potential benefit for the end-user and stakeholders involved in the rehabilitation. Under the ReHyb project, DTU has been investigating virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) as the technological medium to enable end users to conduct rehabilitation at home through serious games which provide a more enjoyable and engaging of format in comparison to conventional rehabilitation.
REHYB@DTU: Exploration of VR and AR capabilities for serious game rehabilitation - 22.02.2022. Developing new interfaces for rehabilitation requires the exploration of different technology platforms and their potential benefit for the end-user and stakeholders involved in the rehabilitation. Under the ReHyb project, DTU has been investigating virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) as the technological medium to enable end users to conduct rehabilitation at home through serious games which provide a more enjoyable and engaging of format in comparison to conventional rehabilitation.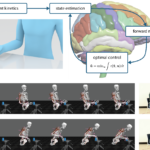 REHYB@TUM: Characterisation of stroke-induced movements using machine learning - 31.01.2022. ReHyb envisions a hybrid exoskeleton which assists users for supporting rehabilitation processes and for activities of daily living. The smart exoskeleton should understand the need of the user and then promote the movements most effective for the training for the “right amount”.
REHYB@TUM: Characterisation of stroke-induced movements using machine learning - 31.01.2022. ReHyb envisions a hybrid exoskeleton which assists users for supporting rehabilitation processes and for activities of daily living. The smart exoskeleton should understand the need of the user and then promote the movements most effective for the training for the “right amount”. REHYB@VALDUCE: Second demo session on exoskeletons - 13.01.2022. The Villa Beretta Rehabilitation Centre, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine of VALDUCE Hospital, has a long-time experience in the testing of innovative technologies for neuro-motor-cognitive rehabilitation. This is the result of a close interaction and sharing experience among the internal team of Physicians, Physiotherapists and Bioengineers and the technical teams of companies, universities and research institutions with which it cooperates.
REHYB@VALDUCE: Second demo session on exoskeletons - 13.01.2022. The Villa Beretta Rehabilitation Centre, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine of VALDUCE Hospital, has a long-time experience in the testing of innovative technologies for neuro-motor-cognitive rehabilitation. This is the result of a close interaction and sharing experience among the internal team of Physicians, Physiotherapists and Bioengineers and the technical teams of companies, universities and research institutions with which it cooperates. Rehyb@ÖSSUR: Intellectual property (IP) considerations - 10.11.2021. In a highly innovative project like ReHyb, it is important to manage novel outcomes and secure potential intellectual property (IP). To this end ReHyb has set up an IP Management Plan to systematically assess the knowledge created within the project. This work has already resulted in several outcomes being assessed, some of which have moved to a preparatory phase for patent applications.
Rehyb@ÖSSUR: Intellectual property (IP) considerations - 10.11.2021. In a highly innovative project like ReHyb, it is important to manage novel outcomes and secure potential intellectual property (IP). To this end ReHyb has set up an IP Management Plan to systematically assess the knowledge created within the project. This work has already resulted in several outcomes being assessed, some of which have moved to a preparatory phase for patent applications.  ReHyb@ICL: New portable wrist robotic interface - 21.09.2021. In the ReHyb project, the Human Robotics Group at ICL aims at modelling the hand neuromechanics of stroke patients and their internal states that are not directly observable. These models will then be used to inform the control algorithm of the hybrid prosthesis to provide a personalized and adaptive assistance during activities of daily living and rehabilitative training.
ReHyb@ICL: New portable wrist robotic interface - 21.09.2021. In the ReHyb project, the Human Robotics Group at ICL aims at modelling the hand neuromechanics of stroke patients and their internal states that are not directly observable. These models will then be used to inform the control algorithm of the hybrid prosthesis to provide a personalized and adaptive assistance during activities of daily living and rehabilitative training.  ReHyb@Stelar: ReHyb approach on GDPR compliance - 14.09.2021. Big data has changed the way we manage and analyze data in the healthcare industry. Using modern big data techniques can lead to better patient care, an improvement of the quality of life of patients, offer better predictions for difficult to diagnose diseases, and more. For such solutions to work, however, sensitive patient data often need to be collected and analyzed.
ReHyb@Stelar: ReHyb approach on GDPR compliance - 14.09.2021. Big data has changed the way we manage and analyze data in the healthcare industry. Using modern big data techniques can lead to better patient care, an improvement of the quality of life of patients, offer better predictions for difficult to diagnose diseases, and more. For such solutions to work, however, sensitive patient data often need to be collected and analyzed.  ReHyb@SK: Pilot studies with patients started -
11.08.2021. With years of experience in scientifically exploring and evaluating device-based therapies, the role of Schoen Clinic Bad Aibling – Harthausen in the ReHyb project is to accompany and evaluate the technical integration of the ReHyb system from a user perspective. Such a user-centered approach is repeatedly said to be important for successful rehabilitation and targets to include the opinions and needs of patients.
ReHyb@SK: Pilot studies with patients started -
11.08.2021. With years of experience in scientifically exploring and evaluating device-based therapies, the role of Schoen Clinic Bad Aibling – Harthausen in the ReHyb project is to accompany and evaluate the technical integration of the ReHyb system from a user perspective. Such a user-centered approach is repeatedly said to be important for successful rehabilitation and targets to include the opinions and needs of patients.