 REHYB@SSSA: Exoskeletons for upper-limb rehabilitation - 30.06.2021. At the Wearable Robotics Lab of Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna (SSSA), we are working on the design and development of the powered exoskeletons for the ReHyb project. The combination of a shoulder-elbow- and a hand-wrist exoskeleton (namely ReHyb-HP and ReHyb-Hand) will allow patients with moderate to severe upper-limb movement limitations to carry out rehabilitation treatments in clinic, receiving adaptive support for functional mobilization of the arm and assistance in grasping tasks.
REHYB@SSSA: Exoskeletons for upper-limb rehabilitation - 30.06.2021. At the Wearable Robotics Lab of Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna (SSSA), we are working on the design and development of the powered exoskeletons for the ReHyb project. The combination of a shoulder-elbow- and a hand-wrist exoskeleton (namely ReHyb-HP and ReHyb-Hand) will allow patients with moderate to severe upper-limb movement limitations to carry out rehabilitation treatments in clinic, receiving adaptive support for functional mobilization of the arm and assistance in grasping tasks.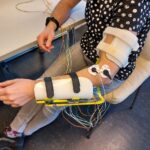 REHYB@TECNALIA: Integration of FES and EMG technologies to improve usability aspects - 31.05.2021. In the ReHyb project TECNALIA focuses on development and integration of multichannel Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) and Electromyography (EMG) technologies into the ReHyb exoskeleton systems. We are developing a new, distributed wrist and hand neuroprosthesis that synergistically works together with a wearable exoskeleton.
REHYB@TECNALIA: Integration of FES and EMG technologies to improve usability aspects - 31.05.2021. In the ReHyb project TECNALIA focuses on development and integration of multichannel Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) and Electromyography (EMG) technologies into the ReHyb exoskeleton systems. We are developing a new, distributed wrist and hand neuroprosthesis that synergistically works together with a wearable exoskeleton. 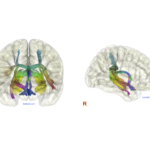 REHYB@IBEC & SPECS-Lab: Will power is key to learning and memory - 23.04.2021. The SPECS Lab at IBEC has identified, for the first time in humans, the physiological mechanism responsible for effective learning processes based on self-motivation and freedom of choice.
REHYB@IBEC & SPECS-Lab: Will power is key to learning and memory - 23.04.2021. The SPECS Lab at IBEC has identified, for the first time in humans, the physiological mechanism responsible for effective learning processes based on self-motivation and freedom of choice.  REHYB@DTU: Upper-limb exoskeleton prototype utilizing Lego Technic components - 25.03.2021. Technical University of Denmark has the responsibility for designing the interfaces between the human stroke patient and the computers and robotics that form the hybrid exoskeletal neuroprosthesis. To understand the interactions between the patients and technology, a master candidate, Barnabás Homola, developed an upper-limb exoskeleton prototype utilizing Lego Technic components.
REHYB@DTU: Upper-limb exoskeleton prototype utilizing Lego Technic components - 25.03.2021. Technical University of Denmark has the responsibility for designing the interfaces between the human stroke patient and the computers and robotics that form the hybrid exoskeletal neuroprosthesis. To understand the interactions between the patients and technology, a master candidate, Barnabás Homola, developed an upper-limb exoskeleton prototype utilizing Lego Technic components.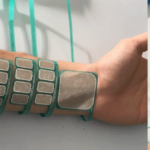 REHYB@TUM: Bringing back lost hand movement capabilities after stroke - 06.03.2021. Functional electrical stimulation (FES) is a treatment that artificially activates muscles during exercise and activity for patients with motor disabilities. This is achieved by placing electrodes on the skin's surface and transmitting low-energy electrical pulses through the body to induce muscle contraction in the stimulated limbs.
REHYB@TUM: Bringing back lost hand movement capabilities after stroke - 06.03.2021. Functional electrical stimulation (FES) is a treatment that artificially activates muscles during exercise and activity for patients with motor disabilities. This is achieved by placing electrodes on the skin's surface and transmitting low-energy electrical pulses through the body to induce muscle contraction in the stimulated limbs. REHYB@VALDUCE: Interactive demo session - 31.01.2021. The Villa Beretta Rehabilitation Centre, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine of VALDUCE Hospital, is equipped with high technological devices for evaluation of patients’ functions as well as for customized rehabilitation treatments.
REHYB@VALDUCE: Interactive demo session - 31.01.2021. The Villa Beretta Rehabilitation Centre, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine of VALDUCE Hospital, is equipped with high technological devices for evaluation of patients’ functions as well as for customized rehabilitation treatments.  REHYB@STELAR: Sensitive data and user privacy - 19.01.2021. The ReHyb project aims at developing a digital twin respecting Ethics and Data Protection. A digital twin is a digital replica of a living or non-living physical entity and it enables a seamless transfer of data by connecting physical and virtual worlds. In this regard, it is clear that such innovative ideas and tools need to achieve trust from the users and the best way is being transparent and showing that the project has checked and assessed all ethical and Data Protection issues.
REHYB@STELAR: Sensitive data and user privacy - 19.01.2021. The ReHyb project aims at developing a digital twin respecting Ethics and Data Protection. A digital twin is a digital replica of a living or non-living physical entity and it enables a seamless transfer of data by connecting physical and virtual worlds. In this regard, it is clear that such innovative ideas and tools need to achieve trust from the users and the best way is being transparent and showing that the project has checked and assessed all ethical and Data Protection issues. REHYB@IUVO: Novel shoulder-elbow exoskeleton’s design - 23.12.2020. At IUVO labs, the R&D team is working on the design and development of a fully portable and extremely lightweight shoulder-elbow exoskeleton to support the upper limb movements in post-stroke patients with mild to moderate hemiparesis.
REHYB@IUVO: Novel shoulder-elbow exoskeleton’s design - 23.12.2020. At IUVO labs, the R&D team is working on the design and development of a fully portable and extremely lightweight shoulder-elbow exoskeleton to support the upper limb movements in post-stroke patients with mild to moderate hemiparesis. REHYB@ÖSSUR: Identifying user groups - 30.11.2020. The ReHyb project aims at providing solutions that can assist in rehabilition of upper limbs and to provide assistance in ADL to persons that have finished rehabilitation.
REHYB@ÖSSUR: Identifying user groups - 30.11.2020. The ReHyb project aims at providing solutions that can assist in rehabilition of upper limbs and to provide assistance in ADL to persons that have finished rehabilitation. 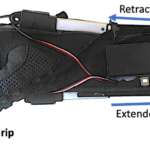 REHYB@ICL: Hand Exoskeleton Enables Patient to Practice Task-Specific Exercises with a Therapist - 27.10.2020. Imperial College London, European Neurosciences Center / Centro Europeo de Neurociencias (CEN) and the University of Toronto have created an intercontinental partnership to study the clinical applications of fully integrated wearable exoskeletons.
REHYB@ICL: Hand Exoskeleton Enables Patient to Practice Task-Specific Exercises with a Therapist - 27.10.2020. Imperial College London, European Neurosciences Center / Centro Europeo de Neurociencias (CEN) and the University of Toronto have created an intercontinental partnership to study the clinical applications of fully integrated wearable exoskeletons.